Data analytics has accompanied me for 15 years already. I started my career as a data analyst in a controlling department immediately following my graduation from the University of West Bohemia; I now work as a data scientist providing consultancy services for a range of different fields. The data analysis itself is the funny part. It provides a lot of valuable information to enable the data driven decisions. However, the most important step in the whole data analytics or data science process is communicating the results effectively.
The original article you can find here
1. Why is data visualization important?
Visualization is a kind of new language which serves for communication within the organizations across all levels “translating” the information the analyst has discovered from the data into a visual context that can be easily understood by the business user.
Today, everyone is talking about digital transformation, where across the world, especially the internet world, data is being generated. However, data itself does not help us. We have to convert it into something valuable.
We must build a big data environment that surfaces actionable business intelligence in a way that is easy to understand. Good data visualizations are key to showing insights and features that are difficult to point out in a raw table. They make it easier for users to detect patterns, trends, and outliers.
To summarize, here are the reasons why visualizing data is important:
- Understanding data
- Communicating results and information
- Extracting knowledge
- Telling a story
- Making data-driven decisions
There are common visualization principles we should always consider when creating the outputs:
- Know your audience
- Set the goals
- Select the right visualization type
- Simplify
- Emphasize
- Storytelling
2. Is my data unimodal, bimodal, or multimodal?
In data visualization there we can talk about different types of visualization. The first split is based on the character of the data – if it is unimodal, bimodal or multimodal.
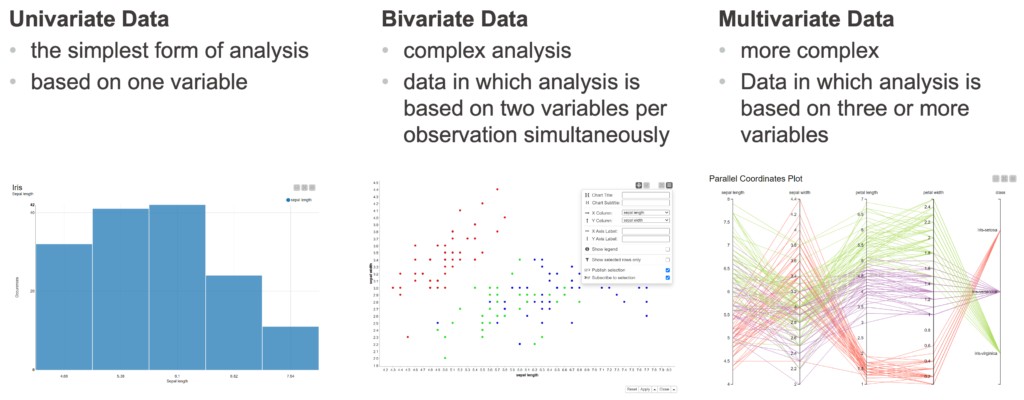
- Univariate analysis – each variable is analyzed individually and we don’t look at more than one variable at a time. Univariate is used for the simplest form of analysis. It is the type of data in which analysis are made only based on one variable only
- Bivariate analysis – we analyze two variables to explore the association between them
- Multivariate analysis – handles more than two variables and is for dealing with multi-dimensional data
3. Choose the visualization type
Another common split is based on visualization type. We can see three main categories: Tables, Charts, Dasboards.
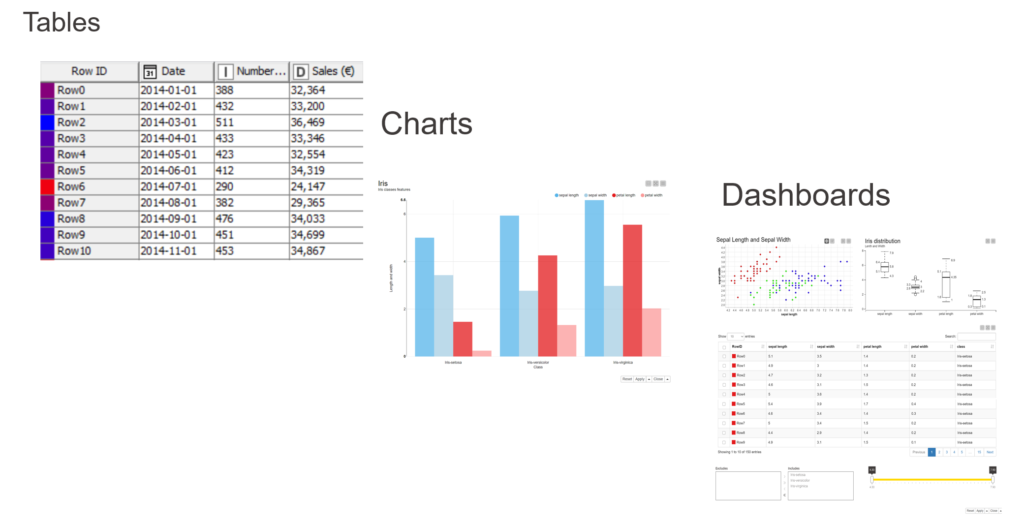
Tables
Tables are a two-dimensional array-like structure in which each column contains values of one variable and each row contains one set of values from each column. Rows include observations and are always in a standard structure, where the structure is given by the columns, illustrating values of different features of each observation. Tables enable accurate searches of a certain value or values.
Charts
Charts illustrate data in graphs or plots. It’s very important to select the right visualization type. Here are three most common types and charts:
- Evolution: Shows how a certain series develops with respect to a second quantity
- Line plot, area chart, bar chart (vertical)
- Distribution: enables to illustrate how the data is distributed and compare data to learn how they differ from each other
- Bar chart, histogram,
- Box plot, Violin plot, statistical indicators
- Relation: shows (the strength of) a relationship between two variables
- Scatter plot, heatmap, bubble chart
Dashboards
Dashboards contain different visualizations. They are interactive and the dashboard should be sharable via some internal server.
When we have completed the data analysis results, we need to ask ourselves “how should I present them?”. Very often people just take a screenshot of the charts and present them via PowerPoint presentation, or even worse – a PDF.
The problem here is that this is a static representation of the results and they cannot be presented in real time. We can only show the past . Today, it is important to have the data and results available NOW and present them in real time.
Run as a web application
When we run our visualizations as a web application we are able to have the data and the results available immediately and present in real time. The KNIME ecosystem enables this via the KNIME WebPortal.
The KNIME WebPortal enables sharing the data visualization results within the Component and its Composite View and thus bring users a workflow in KNIME available as a web application that is
- Simple to read as a single web page
- Interactive
- Customizable to match corporate design
Before deploying the dashboard of different visualizations to the KNIME WebPortal, we need to understand an important feature in KNIME: the “component”.
What is a component?
Components are nodes to bundle functionality with their own configuration and composite views. Similar to “metanodes”, components are containers of a part of your workflow to build cleaner and structured workflows with the big difference being that the purpose of the components is also to share and then reuse as a template and make them accessible via custom interactive composite views.
The composite view serves for layouting interactive dashboards that can be shared in the KNIME WebPortal as a web application.The layout for the composite view is built in an opened component and can be set up as a:
- Basic layout
- Visual layout
- Advanced layout
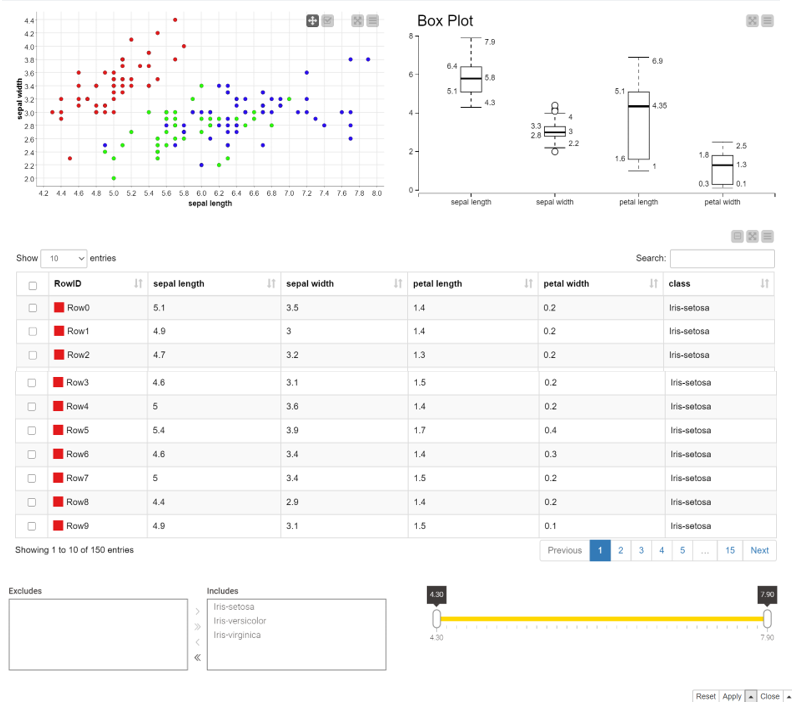
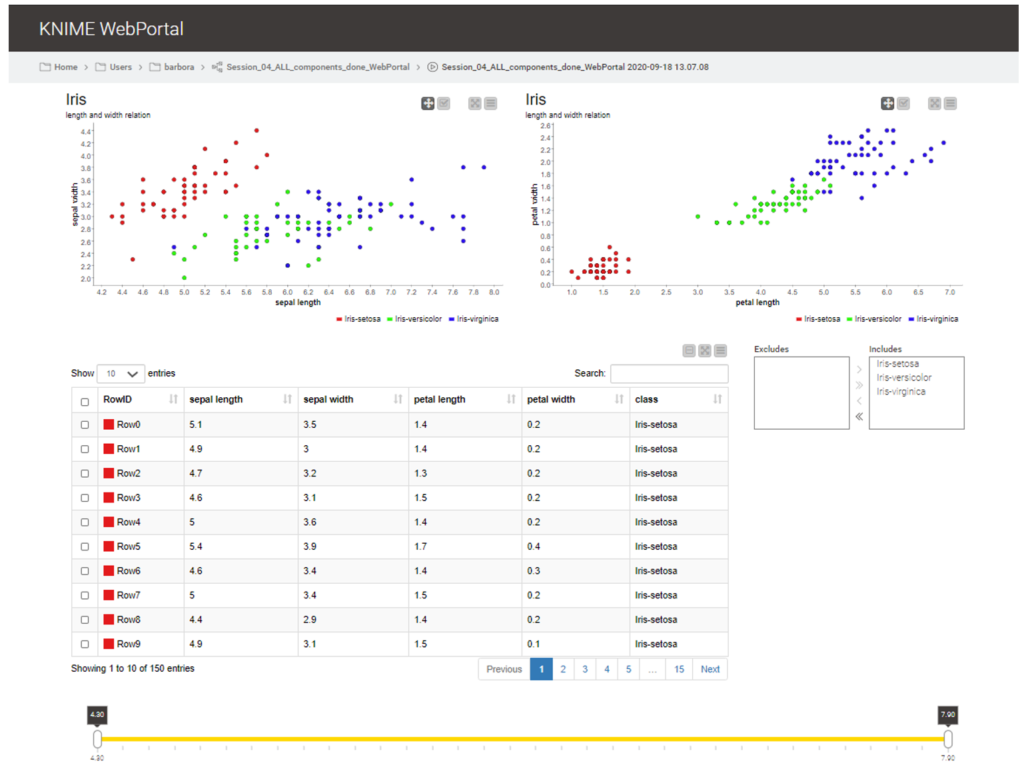
The dashboard is available in KNIME Analytics Platform as an interactive view of the component. The final dashboard can be deployed to the KNIME Server and then shared via the KNIME WebPortal as a web application with your team. Below you can see the composite view in Fig. X. The next screenshot in Fig. X shows the this composite view as a dashboard displayed via the WebPortal.
Do you want to learn more?
Barbora Stetinova is running an online course all about Codeless Data Exploration and Visualization on December 7-11, 2020. Sign up for this course and benefit from a 20% discount by entering the promotional code L4-DV-1220 when you register here.

About Barbora Stetinova
Barbora has worked in the Automotive Industry for many years and has extensive experience in data science, machine learning and business intelligence, leading small teams, controlling, and developing strategical projects. She develops and publishes e-learning courses for Udemy and other similar platforms and cooperates on e-learning projects with Packt Publishing Hub that focus on data science with Python and KNIME Analytics Platform. She is motivated by learning new things, achieving goals, and helping others.



